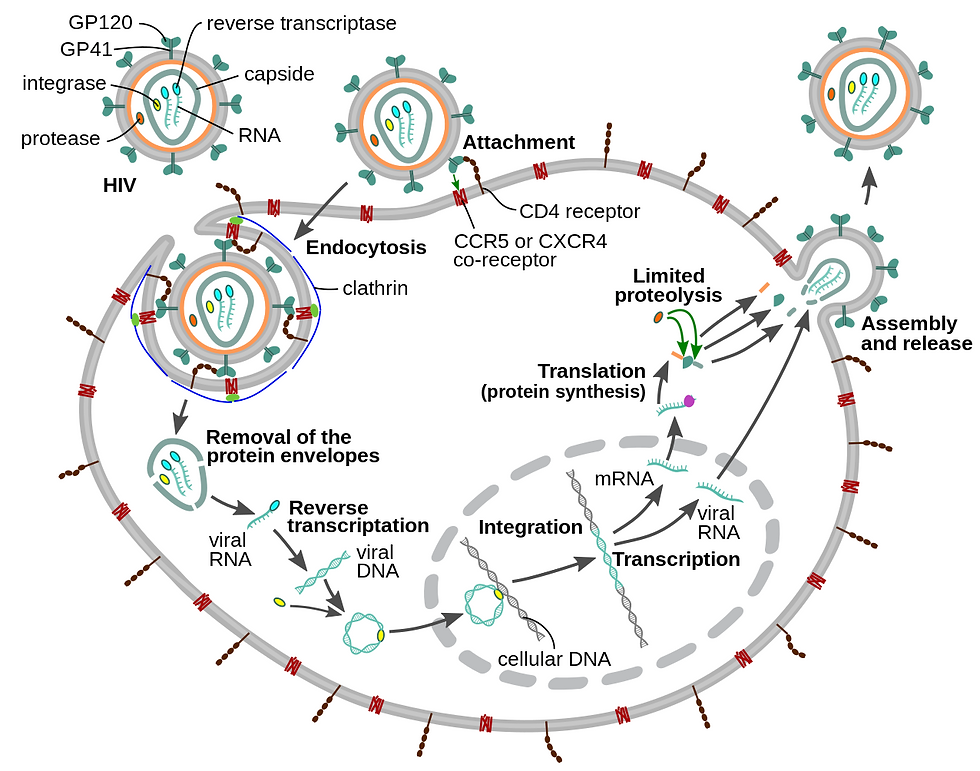
HIV
HIV is a retrovirus with an outer envelope containing gp20 and gp41. It's capsid is composed of p24, and contains RT (Reverse Transcriptase), Protease, Integrase, and 2 RNA strands. The p24 is what is tested for a diagnosis.
It's transmitted via:
Contact of bodily fluids e.g. blood, breastmilk, vaginal secretions, and semen
Vertical from mother to child
The risk of transmission is increased with Unprotected sex (anal sex is the highest risk), STI’s, IVDU, transfusions, needle-stick injuries
Early diagnosis and treatment is crucial as, when on ART with a low viral load, patients will have a very low chance of transmitting it to their sexual partners.
Life Cycle
1st phase - Attachment and Entry - Involves CD4 receptors, gp120, gp41, and CCR5/CXCR4 co-receptors
Fusion/Entry inhibitors act here
2nd phase - Reverse transcription and Integration - Involves RT and Integrase
RT Inhibitors and Integrase inhibitors act here
3rd phase - Transcription and Translation - Involves Protease
Protease inhibitors act here
4th phase - Assembly and Budding
Investigations
Tests available:
At-home test
Nucleic Acid Test (NAT) - Also used to screen newborns
ELISA - Tests for presence of HIV antibody and p24
Rapid point-of-care - Finger-prick/Mouth swab, but a serological confirmation is still needed
Important investigations to do are Viral load and CD4 count!
Management
ART!
Backbone of 2 different NRTIs (nucleotide RT inhibitors) + 1 drug of choice (options include protease/integrase inhibitors, and non-NRTIs)
N.B. ART = Antiretroviral therapy. ART is given to all patients, irrespective of viral load or CD4 count.
Prevention
Barrier protection
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) - Use of ART in those at high risk of acquiring HIV
Post-exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) - Short-term use (up to 72hrs) of ART after potential exposure
ART for all pregnant women with HIV - To prevent vertical transmission
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
This is an advanced stage of HIV where there’s evidence of an AIDS-defining illness + CD4 count < 200.
The main AIDS-defining illnesses to know include:
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) - fungal infection, commonly affecting lungs
Always have this as a differential in any immunocompromised patient presenting with a persistent dry cough and oxygen desaturation on minimal exertion.
Patients are given prophylaxis with Co-trimoxazole (Septrin)
Kaposi’s sarcoma - most common tumour in HIV
TB,
CMV infection Lymphoma, Candidiasis, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptococcosis (fatal fungal pneumonia or meningitis), Cryptosporidiosis
Other less common AIDS-defining illnesses are CMV infection Lymphoma, Candidiasis, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptococcosis (fatal fungal pneumonia or meningitis), and Cryptosporidiosis.
Important Links:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hiv-and-aids/
https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/555"Pneumocystis pneumonia: These chest radiographs are of two patients. Both show -ground glass appearance. The left chest X-ray (CXR) shows a much more subtle ground-glass appearance while the right CXR shows a much more gross ground-glass appearance mimicking pulmonary edema.” © Carolyn M. Allen, Hamdan H. AL-Jahdali, Klaus L. Irion, Sarah Al Ghanem, Alaa Gouda, and Ali Nawaz Khan CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
“Pneumocystis pneumonia: Lung cysts are usually multiple and bilateral, but range in size, shape and distribution. They are more commonly appreciated on computed tomography (CT)/high-resolution CT” © Carolyn M. Allen, Hamdan H. AL-Jahdali, Klaus L. Irion, Sarah Al Ghanem, Alaa Gouda, and Ali Nawaz Khan CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)