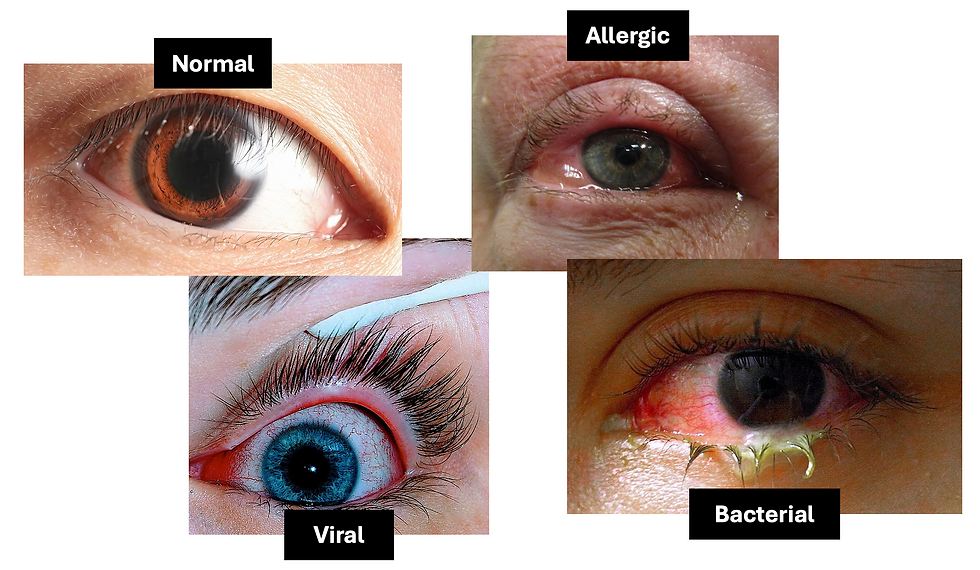
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis typically presents with:
Red, itchy eye + discharge
No photophobia or vision loss
Allergic conjunctivitis
Presentation:
Red eyes with very serous discharge, and chemosis if severe
Symptoms are seasonal or occur when exposed to allergens
Management:
Avoid allergen and use artificial tears (dilutes the allergen)
Topical antihistamines may be given if conservative measures fail
Viral conjunctivitis
Presentation:
Red eyes with very serous discharge, but is more likely to be unilateral
Management:
Self-limiting, so treated with good eye hygiene, use of artificial tears, and regular hand hygeine
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Causes:
Staphylococcus epidermis, Staph aureus, Strep pneumoniae and H.influenzae, Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea (take a sexual hx if suspected)
Presentation:
Red, itchy eyes with purulent discharge
Eyelids ‘stuck’ together in the morning
Management:
Self-limiting and resolves in 7 – 14 days, so eye drops can be used for lubricating, symptomatic relief
In severe cases, topical chloramphenicol can be given
Important Links:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/conjunctivitis/ https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/conjunctivitis-infective/
https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/68 “Anterior view of an Asian male human eye, showing light brown iris with a prominent and dark limbal ring. The pupil is in a semi dilated state.” © Rapidreflex CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
“Allergic conjunctivitis showing conjunctival edema” © James Heilman, MD CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
“A swollen, pus-filled eye with conjunctivitis.” © Tanalai CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
“An eye infected with viral conjunctivitis” © Joyhill09 CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)