Gout and Pseudogout
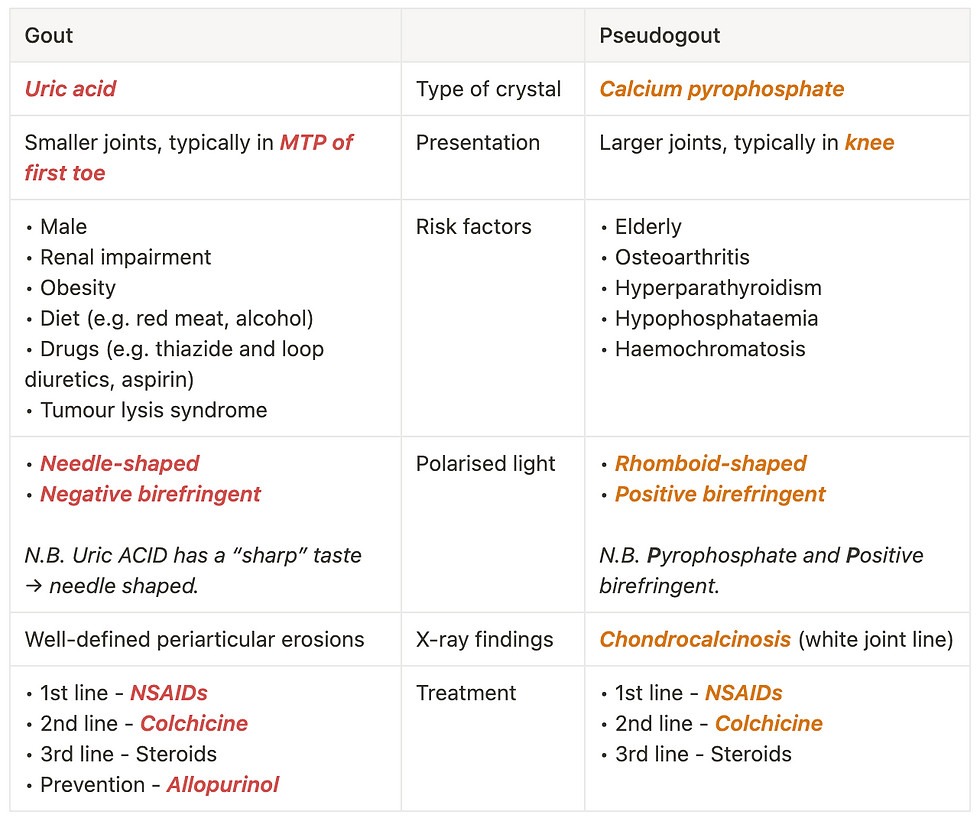
Gout is formed of Uric acid crystals. Pseudogout is formed of Calcium pyrophosphate crystals. Both present with a hot, swollen, stiff, painful joint, but a key differential of septic arthritis needs to be ruled out first!
Investigations
Joint aspiration is needed for a definitive diagnosis. A polarised light microscopy is done subsequently to differentiate between the 2 types:
Uric acid crystals - Needle-shaped, Negative birefringent (NN)
Calcium pyrophosphate crystals - Rhomboid-shaped, Positive birefringent
To differentiate it from septic arthritis, MC&S will show:
No bacteria (presence of bacteria → septic arthritis)
Raised WCC (a much higher value → septic arthritis)
XR may show Chondrocalcinosis as a thin white line in the joint space.
Bloods:
Uric acid – Lowering the levels of this (e.g. w/allopurinol), will reduce the risk of further attacks
U&E – Renal impairment is a risk factor for gout
N.B. Thiazide and loop diurectics, Low-dose aspirin, and Chemotherapy can cause hyperuricaemia, therefore increasing the risk of gout.
Management
Acute attack:
Supportive as symptoms usually resolve over several weeks
NSAIDs
Colchicine is an alternative if NSAIDs contraindicated e.g. CKD, but it carries a high risk of GI disturbance, esp. diarrhoea
Steroids if stage 5 CKD
Prophylactic - Allopurinol (1st line)
N.B. Co-prescribe a PPI for those at high risk of GI complications.