Upper Limb Disorders
Wrist Fractures
The most common mechanism of this injury is FOOSH = Fall onto an outstretched hand.
Colle's fracture is a transverse fracture of the distal radius, causing the distal portion to displace posteriorly
Scaphoid fracture presents with tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox. The complication that can occur here is Avascular necrosis as the scaphoid bone only has a single blood supply, so a fracture can cut this off.
Shoulder Dislocation
This is most commonly an Anterior dislocation.
A key complication here is Axillary nerve (C5, C6) damage, which will present with sensory loss over the lateral deltoid, and motor loss of deltoid and teres minor. Another complication that can occur here is a Rotator cuff tear.
When examining these patients, it's always very important to check for vascular and nerve damage; pulses, sensation, movement.
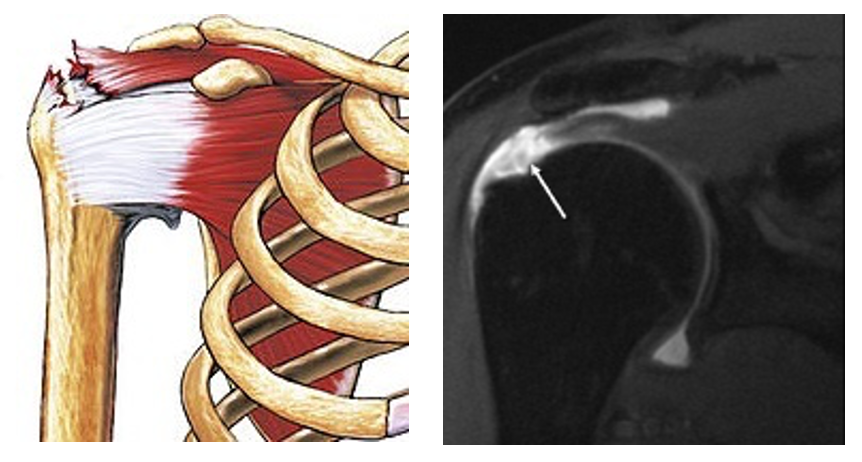
Rotator Cuff Tear
Muscles involved are - SITS:
Supraspinatus (abduction)
I
nfraspinatus (external rotation)
Teres Minor (external rotation)
Subscapularis (internal rotation)
A tear of a muscle here can either be due to an acute injury or age-related degenerative changes e.g. tennis.
Imaging - US or MRI
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
Inflammation and fibrosis of joint lead to adhesions (scarring), which bind and tighten the capsule around the joint and restrict its movement. A key risk factor for this occuring is Diabetes Mellitus.
2 types:
Primary – spontaneous w/o a trigger
Secondary – response to trauma, surgery, or immobilisation
It tends to present with:
Gradual onset pain and stiffness of the shoulder with reduced movement
Pain worsens initially and persists for weeks-months
Stiffness can persist for months-years
Symptoms gradually resolve over time
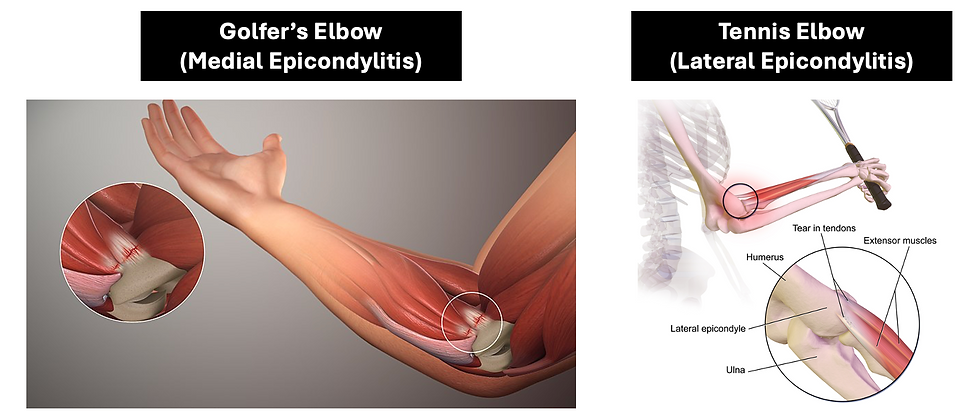
Epicondylitis
This is a type of repetitive strain injury.
2 types:
Lateral epicondylitis (Tennis elbow)
Medial epicondylitis (Golfer’s elbow)
It presents with pain and tenderness at the epicondyle, and weakness in grip strength.
Olecranon Bursitis
Inflammation of bursa, which causes swelling. This can be caused by:
Repetitive damage e.g. leaning on elbow
Trauma
RA or Gout
Infection (Septic bursitis)
It presents with a swollen, warm, tender, fluid-filled joint bursa.
It's managed with Rest, Analgesia, Ice, Compression, and Aspiration.
DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis
This is a type of repetitive strain injury e..g. thumb abduction in office workers or musicians.
This is where there's inflammation and swelling of the tendons of the Abductor pollicis longus and Extensor pollicis brevis at the base of the thumb.
It presents with pain on the radial side of the wrist, weakness, numbness, and tenderness.
Trigger Finger
Flexor tendons of fingers pass through several sheaths. Trigger finger is where there’s thickening/tightening of these sheaths, therefore preventing the tendon moving under it smoothly.
It presents with:
Pain and tenderness
Popping or clicking sound
Finger gets stuck in flexed position
Important Links:
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/distal-radius-fractures-broken-wrist/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/dislocated-shoulder/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/rotator-cuff-tears/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/frozen-shoulder
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/tennis-elbow-lateral-epicondylitis/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/elbow-olecranon-bursitis/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/de-quervains-tendinosis
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/trigger-finger/ “X-ray of a colles fracture of the left wrist accompanied by an ulnar styloid fracture.” © Lucien Monfils CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
“Fracture across waist of scaphoid bone (indicated by arrow).” © Gilo1969 CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
“Dislocated shoulder in X-ray.” © Hellerhoff CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
“Posterior shoulder dislocation in the X-ray (left) with the so-called "light bulb sign". The humeral head is rotated by the tilt at the posterior edge of the glenoid and therefore has a contour reminiscent of a light bulb.” © Hellerhoff CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
“A tear of the supraspinatus muscle, the most common form of rotator cuff tear” © Nucleus Communications CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
MRI of rotator cuff full-thickness tear – Medscape (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Full_Thickness_Tear.jpg)
“Image of frozen shoulder and shoulder capsule” © Spooriak CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
“A 3D medical animation still shot illustrating the medical condition known as Golfer's elbow” © www.scientificanimations.com CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
“Tennis Elbow” © BruceBlaus CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
“Medical illustration of olecranon bursitis - inflammation of the bursa, characterized by redness, swelling and pain at the tip of the elbow.” © InjuryMap CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
Bursitus of the elbow – NJC123 (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bursitis_Elbow_WC.JPG)