Peripheral Mononeuropathies
Brachial plexus (C5-T1) Palsy
Presents with pain, paraesthesia and weakness of affected arm.
Causes - Trauma, radiotherapy, prolonged wearing of a heavy rucksack, cervical rib fracture, thoracic outlet compression
Erb’s Palsy occurs when there's damage to the upper trunk of the brachial plexus (C5, C6), causing weakness of its innervating muscles. It classically presents with the arm in a "waiters tip" position:
Arm adducted – weak shoulder abductors
Elbow extended – weak flexors
Forearm pronated – weak supinators
Wrist flexed – weak extensors
Radial Nerve (C5-T1) Palsy
Main function of this nerve is to open the fist.
Causes include:
Saturday night palsy – Patient sleeping with arm over back of chair - Alcohol is a major factor here
Crutches
Handcuffs
Humeral shaft fracture
Presents with Wrist drop, and complete weakness of arm extensors.
If the palsy is only of its posterior interosseous branch, there'll be weakness of FINGER EXTENSION ONLY w/o wrist drop
Median Nerve (C6-T1) Palsy
This nerve innervates the muscles of precision grip. Risk factors are genetic tendency (biggest factor), pregnancy (more fluid puts pressure on nerves in hand and wrist), trauma, and obesity.
Presentation - Depends on the location of the lesion:
Carpal Tunnel syndrome (Wrist) - Sensory loss of radial 3.5 hand, Weakness of thumb abduction (abductor pollicis brevis)
Anterior Interosseous syndrome - Weakness of 1st and 2nd finger pinch (distal phalanx)
Proximal – may show combined defects
Symptoms are usually exacerbated by sleep, repetitive hand movements or sustained posture, and relieved by shaking the hand or hanging it over the edge of a bed.
Examination - Tinel’s and Phalen’s tests
Management - Splinting, Steroid injections, Decompression surgery
Ulnar Nerve (C7-T1) Palsy
This nerve innervates the intrinsice muscles of the hand. Lesions tend to be at either the elbow (90%) or wrist (10%).
Presentation:
Ulnar Claw - weakness of 4th and 5th fingers
Sensory loss over 5th and half of 4th fingers
Wasting and Dorsal guttering on ulnar side
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (L2-L3) Palsy – Meralgia Paraesthetica
Caused by nerve entrapment under the inguinal ligament.
Presents with anterolateral shooting, burning thigh pain.
Sciatic nerve (L4-S3) Palsy
Presents with:
Weakness of hamstring and all muscle below knee (Foot drop)
Sensory loss below knee laterally
Common peroneal nerve (L4-S1) Palsy
Causes - Trauma, Sitting cross-legged for long periods
Presentation:
Foot drop
Weak foot EVERSION
Sensory loss over dorsal foot
An important differential to consider her is an L4/5 radiculopathy, which would also present with foot drop, but the patient would instead have weak foot INVERSION and back pain.
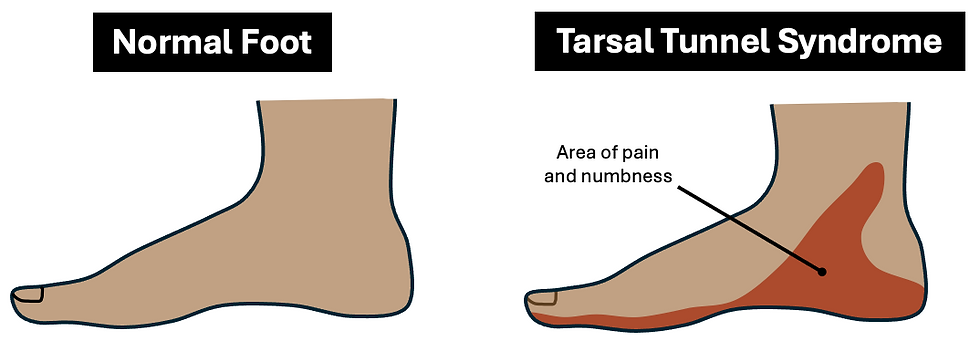
Tibial nerve (L4-S3) Palsy
Presentation:
Weak plantarflexion, foot inversion, toe flexion
Sensory loss over sole of foot
Mononeuritis multiplex
This is the involvement of 2+ peripheral nerves, and is rapidly-evolving.
Its most common cause is Vasculitis, but other causes include DM, RA, SLE, Amyloidosis, Sarcoidosis, Leprosy.
Important Links:
https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/581
https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/380
https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/799 “Photograph of a healthy hand imitating an ulnar claw.” © Mcstrother CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
“Ape Hand Deformity 1” © Emily Barrett CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
“Ape Hand Deformity 2” © Emily Barrett CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/) “Photograph of a healthy hand imitating an ulnar claw.” © Mcstrother CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/) “Nervous System” © Laboratoires Servier CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
“Foot drop” © Pagemaker787 CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)